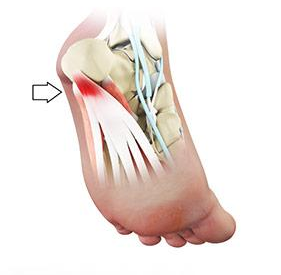
Plantar Fasciitis
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar Fasciitis is a common and uncomfortable problem that causes heel pain.
Plantar Fasciitis refers to inflammation of the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that lies at the bottom of the foot.
It runs from the heel bone to the toe and forms the arch of your foot.
Who Does Plantar Fasciitis Affect
It is most often seen in middle-aged men and women, but may also occur in those who are constantly on their feet.
Cause of Plantar Fasciitis
The plantar fascia functions as a shock absorber and supports the arch of your foot. Excessive pressure over the fascia may strain and tear the tissue causing heel pain.
Repeated overstretching or overuse causes irritation or inflammation of the fascia.
Other risk factors may include
- Obesity,
- Foot arch problems such as flat feet or high arches,
- Activities such as long-distance running,
- Ballet and dance aerobics,
- Occupations that necessitate walking or standing on hard surfaces for a long period, and
- Wearing shoes with poor arch support or thin-soled shoes.
Symptoms of Plantar Fasciitis
The most common symptom is stabbing pain on the bottom of the foot near the heel.
You experience pain when you take your first steps on awakening and it slowly decreases, but may return after standing or walking for long periods.
Diagnosis of Plantar Fasciitis
Patients who suspect they have sustained Plantar Fasciitis should seek a medical consultation. The diagnosis for a Plantar Fasciitis can often include:
Physical examination
A doctor may evaluate the affected part of the Plantar Fasciitis to determine the presence of swelling, a limited range of motion, abrasions, bruising, or other common signs of a Plantar Fasciitis.
Throughout the process you will be asked about past injuries or issues, your level of pain and frequency, and what symptoms have been identified.
Obtain a Full Medical History
You will ask about your symptoms, medical history, any sports participation and activities that aggravate your condition.
Prior injury can elevate an athlete’s risk of sustaining an injury to the foot or ankle. With this in mind, your medical history can help determine if a former condition has increased the likelihood of a given injury being presented.
Medical Imaging
After a physical examination of the foot or ankle, further details may be sought using medical imaging such as an X-ray or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) to help with a final diagnosis.
A comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s foot or ankle allows us to eliminate various possibilities, arrive at a diagnosis, and recommend a treatment plan.
Treatment of Plantar Fasciitis
Most patients with plantar fasciitis are effectively treated using a multi-faceted approach possibly including the following measures:
Medications:
Treatment can include
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce your pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroids can be injected directly into the plantar fascia which may offer pain relief and reduce inflammation.
- Orthotic implants
For Patients
First Visit Guide Price & Payments Social MediaQuick Enquiry
Thank you for contacting us. We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Oops, there was an error sending your message. Please try again later.
Consulting Location
Practice Hours
- Mon - Fri
- -
- Saturday
- -
- Sunday
- Closed